Senior Consultant Cardiologist
MD(Cal), MRCP(UK), FRCP(London), FACC(USA)
Director - Interventional Cardiology,
Head Quality Assurance - Cathlab
B. M. Birla Heart Research Centre, Kolkata

Senior Consultant Cardiologist
MD(Cal), MRCP(UK), FRCP(London), FACC(USA)
Director - Interventional Cardiology,
Head Quality Assurance - Cathlab
B. M. Birla Heart Research Centre, Kolkata


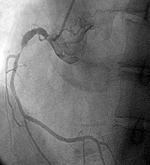 The gradual build up of fat within the blood vessel of the heart causes narrowing and when it becomes significantly narrowed it obstructs adequate blood flow demanded by the heart's muscle leading to demand and supply disparity.
The gradual build up of fat within the blood vessel of the heart causes narrowing and when it becomes significantly narrowed it obstructs adequate blood flow demanded by the heart's muscle leading to demand and supply disparity.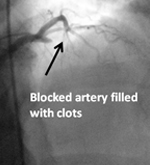 Primary angioplasty is an angioplasty done as a life-saving emergency procedure in a patient with an on-going heart attack.
Primary angioplasty is an angioplasty done as a life-saving emergency procedure in a patient with an on-going heart attack.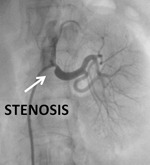 Stenting of blocked renal arteries supplying blood to the kidneys are done in patients who have associated uncontrolled high blood pressure or rapidly worsening kidney function. Blocks in both renal arteries benefit by stenting as it prevents kidney damage progression and in hypertensive patients makes blood pressure control easier.
Stenting of blocked renal arteries supplying blood to the kidneys are done in patients who have associated uncontrolled high blood pressure or rapidly worsening kidney function. Blocks in both renal arteries benefit by stenting as it prevents kidney damage progression and in hypertensive patients makes blood pressure control easier.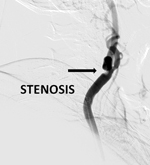 Blood vessels supplying the brain also develops blockages called carotid artery stenosis and such patients usually present to the Neurologist with brain stroke or multiple episodes of transient weakness of arms, legs or slurred speech with rapid improvement known as TIA.
Blood vessels supplying the brain also develops blockages called carotid artery stenosis and such patients usually present to the Neurologist with brain stroke or multiple episodes of transient weakness of arms, legs or slurred speech with rapid improvement known as TIA.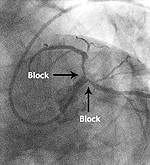 Bifurcation Stenting is done when major blood vessel is diseased and extends into its two major branches, both of which require to be stented along with the main blood vessel. Various complex techniques are available to treat such disease.
Bifurcation Stenting is done when major blood vessel is diseased and extends into its two major branches, both of which require to be stented along with the main blood vessel. Various complex techniques are available to treat such disease.
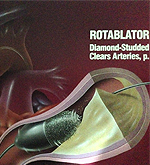 Rotablation is a technique for treating calcified coronary arteries with calcific blockages obstructing passage of balloand and stents for successful angioplasty.
It has a diamond studded head called burr which is made to rotate at a speed of 1,50,000 to 1,90,000 revolution per minute. To prevent the burr from overheating from friction, cold fluid is sprayed continuously during rotablating. This drills through the blocked arteries allowing passage of balloons and proper expansion of stents.
Rotablation is a technique for treating calcified coronary arteries with calcific blockages obstructing passage of balloand and stents for successful angioplasty.
It has a diamond studded head called burr which is made to rotate at a speed of 1,50,000 to 1,90,000 revolution per minute. To prevent the burr from overheating from friction, cold fluid is sprayed continuously during rotablating. This drills through the blocked arteries allowing passage of balloons and proper expansion of stents.
Note :: Due to lack of Data from 1990 to 1995 the exact numbers for the above mentioned procedures are much higher. The data given for the above mentioned procedures are from 1996.
This X-ray is of a gentleman of 54 years who had pacemaker implanted for frequent blackouts due to documented rhythm failure. Was well but suddenly had recurrence of blackouts.
Tests showed normal pacemaker backup, but a new rhythm disturbance (VT) now causing this symptom.
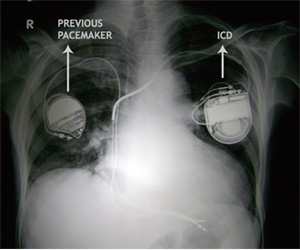
ICD was implanted on the right side. Patient subsequently has received many shocks, but no further blackouts.